his is a motion during which the instantaneous acceleration is always constant.
| (1) |
1)the direction of motion is along a straight line.
2)Average acceleration and instantaneous acceleration have the same magnitude:
By coupling the last relationship with the definition of average acceleration, we can build the velocity law for a uniform acceleration motion
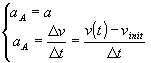
If
| (2) |
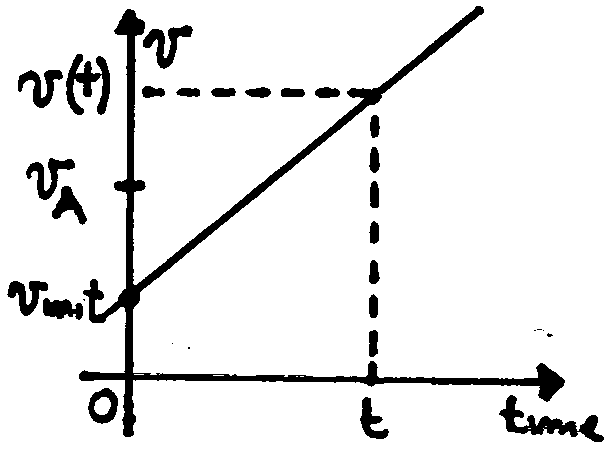
From this graph the relationship between the average velocity and the instantaneous velocity can be deduced. It follows from the idea of a segment’s average point:
By coupling this with the previous equation (2) and with the definition of average speed, we have a three equation system. Its solution represents the law of motion for uniform acceleration motion:
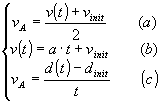
By inserting the (b) into the (a) we have:
and by inserting the (c) into the last one:
that leads to:
| (3) |
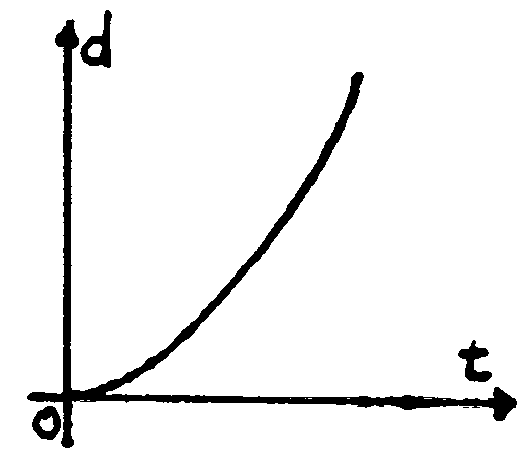
The parabolic behaviour is strictly related to the square dependence on time
No comments:
Post a Comment